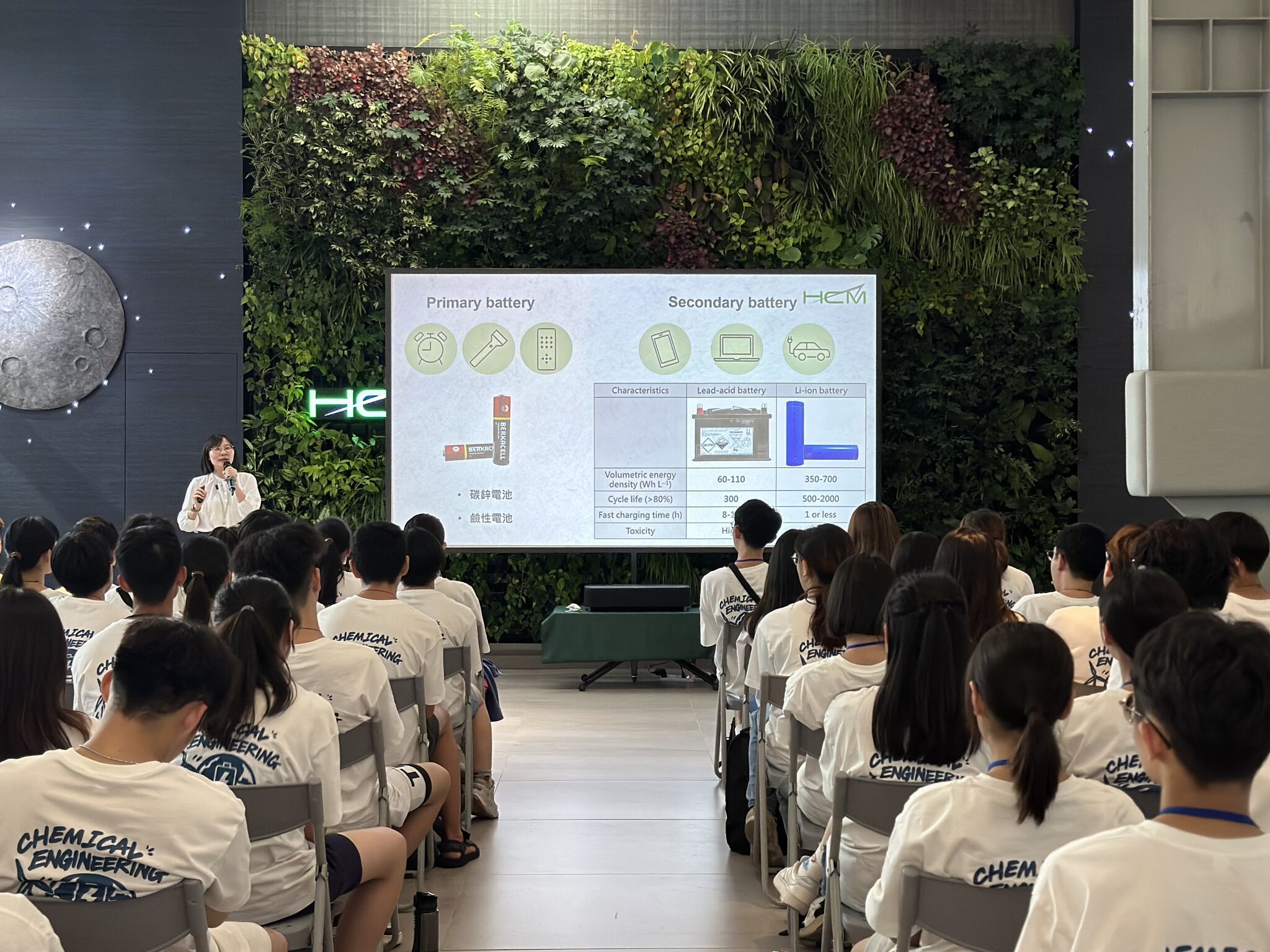
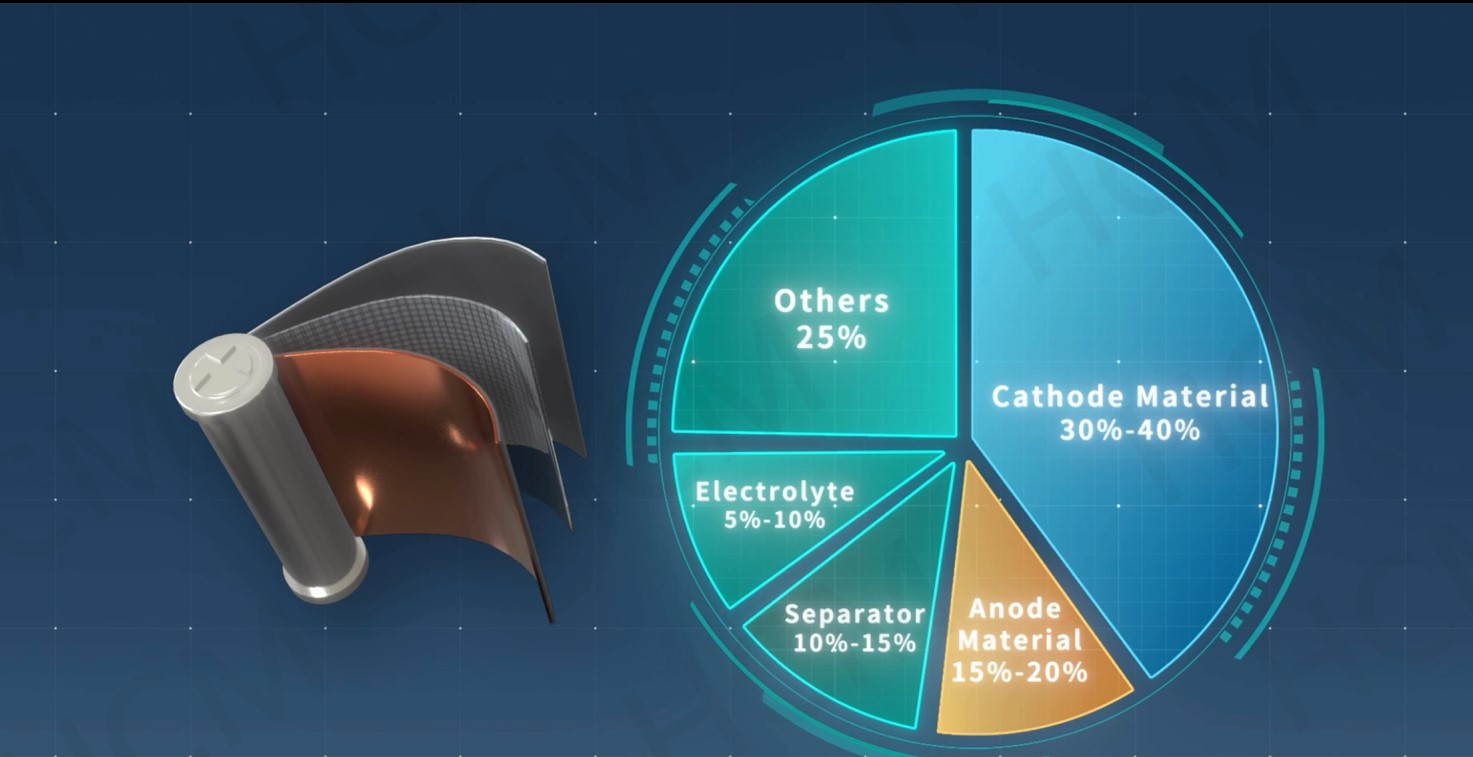
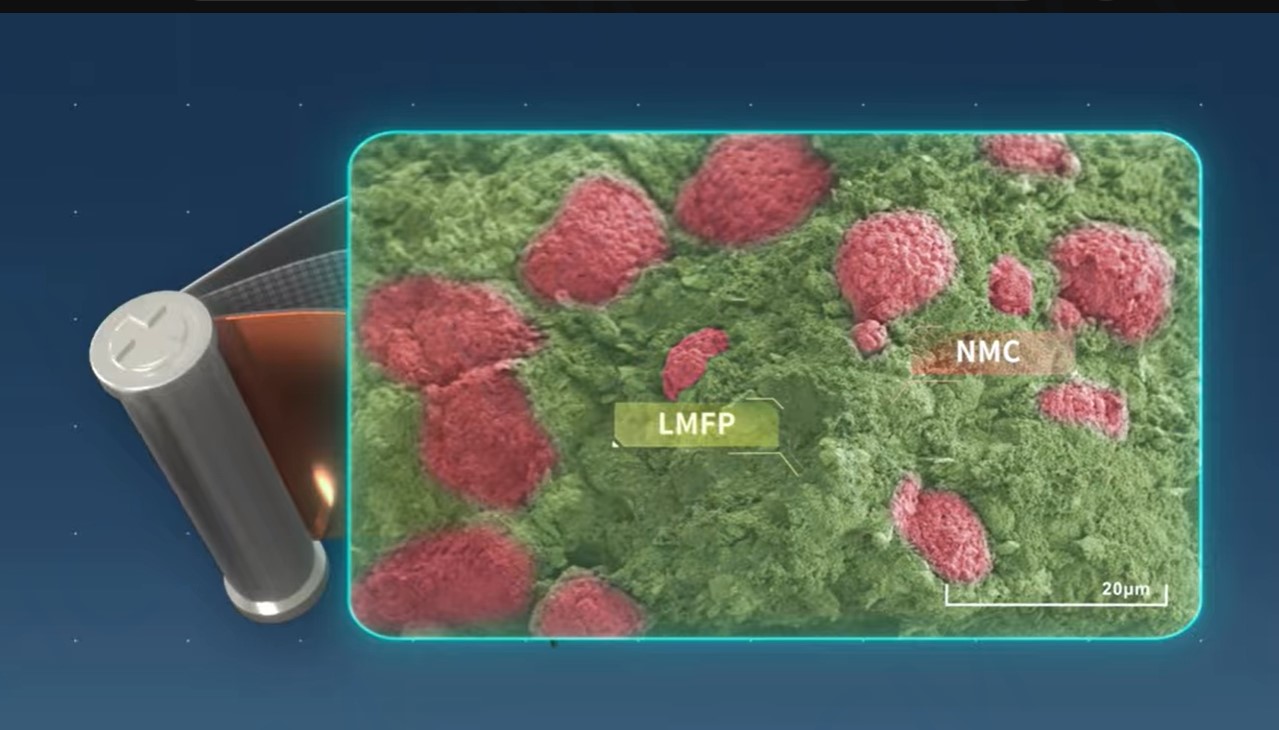
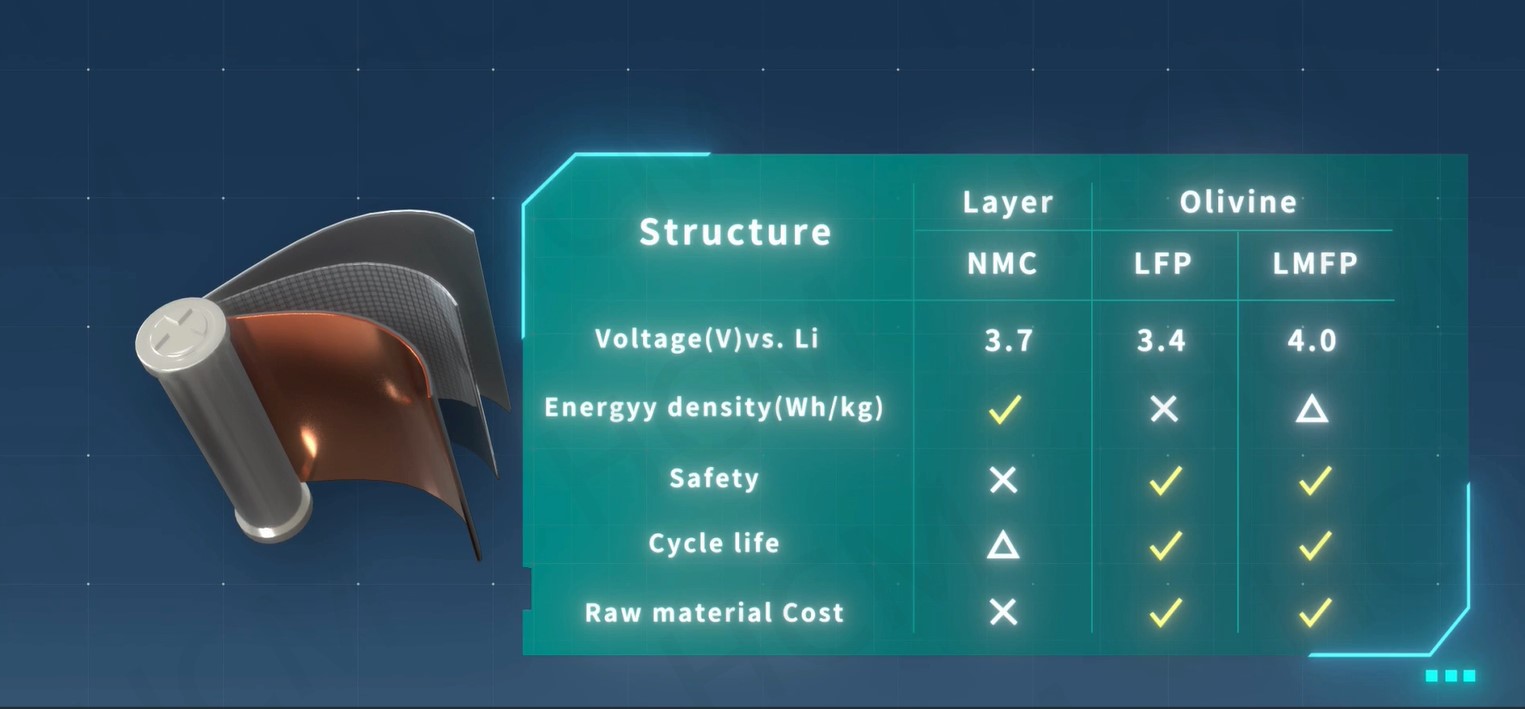
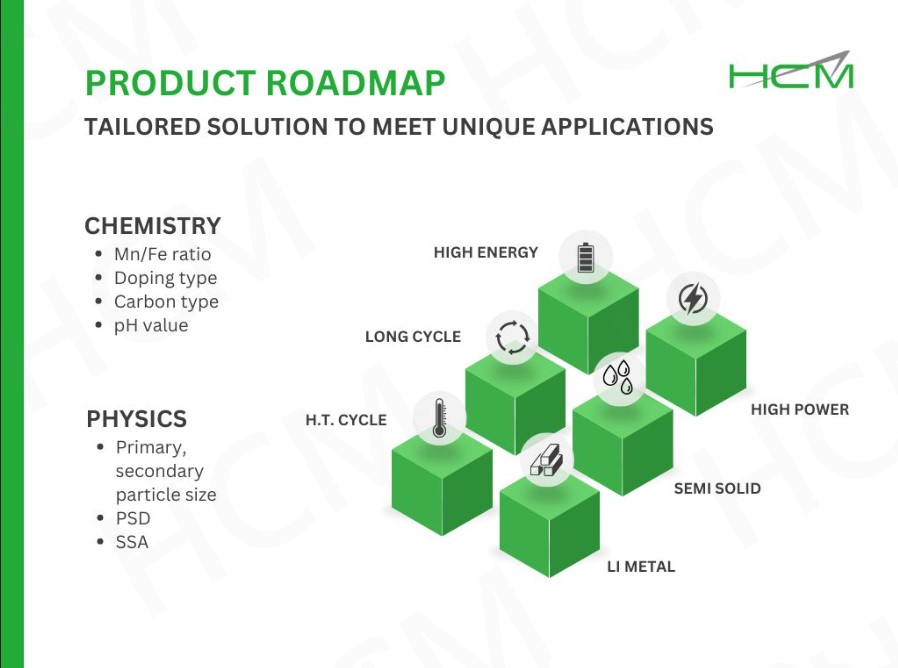
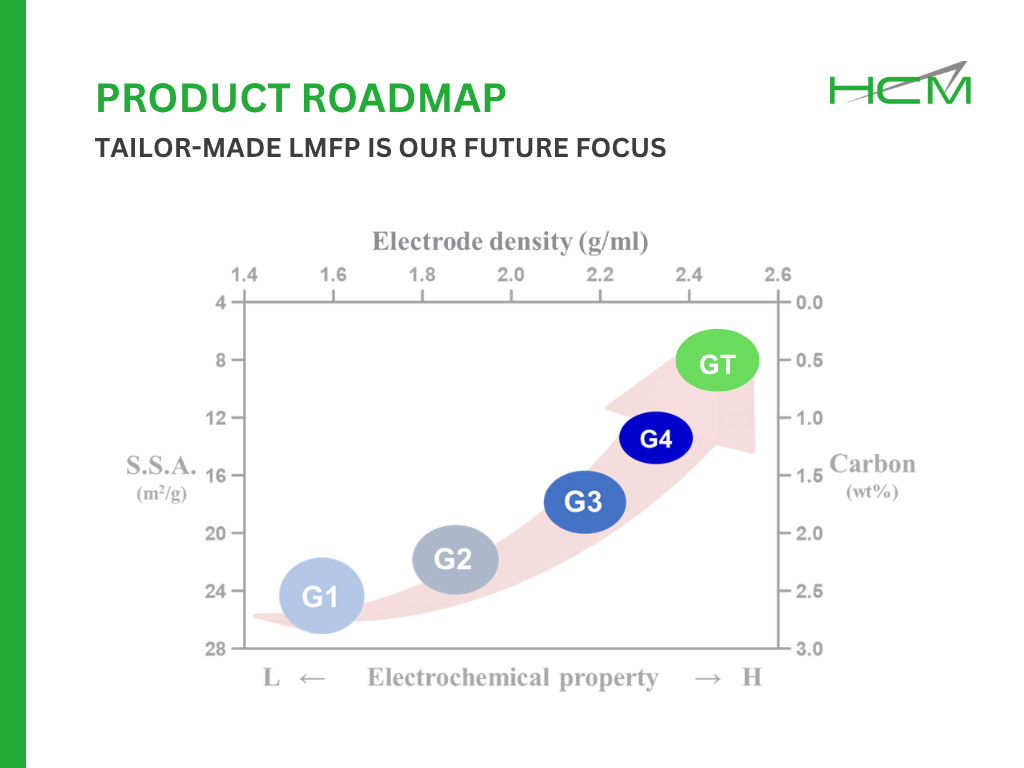
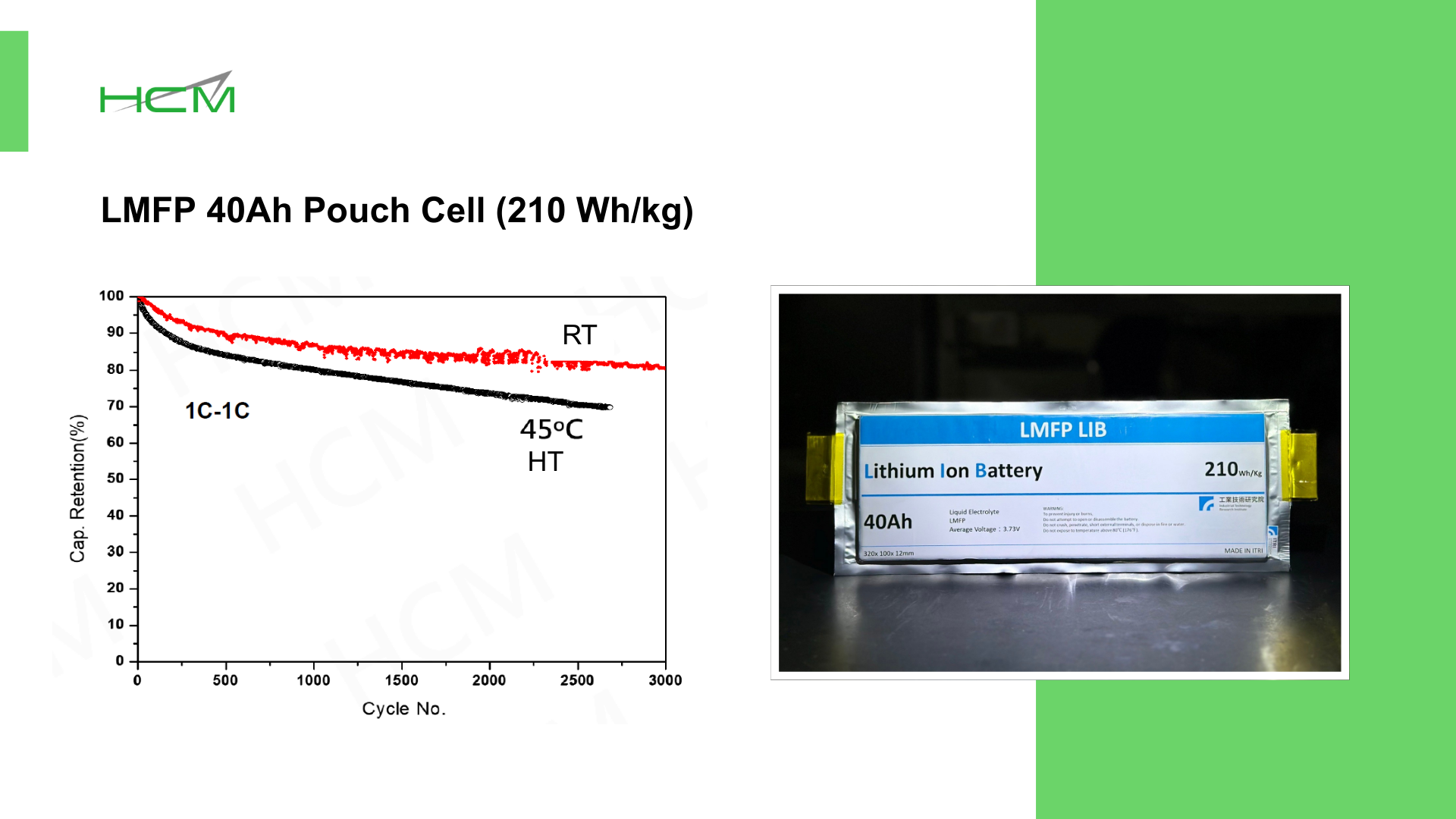
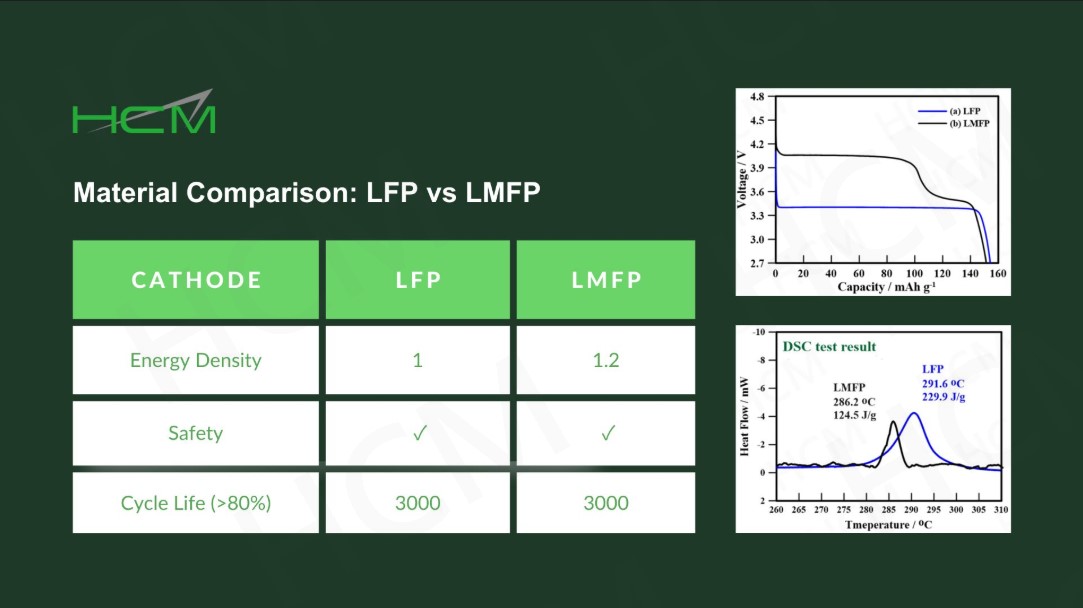
Lithium manganese iron phosphate (LMFP) is a promising cathode material with higher theoretical energy density than LFP. However, its 𝗹𝗼𝘄 𝗟𝗶-𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗱𝗶𝗳𝗳𝘂𝘀𝗶𝘃𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗲𝗹𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗿𝗶𝗰𝗮𝗹 𝗰𝗼𝗻𝗱𝘂𝗰𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗶𝘁𝘆, both significantly lower than LFP, have raised concerns due to their impact on rate capability and overall performance.
At HCM, we have developed multiple approaches to overcome these challenges by engineering both the surface and internal structure of LMFP particles:
1️⃣ 𝗖𝗮𝗿𝗯𝗼𝗻 𝗻𝗮𝗻𝗼𝗰𝗼𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 – provides a uniform conductive network around each particle, reducing resistance and improving electron transport.
2️⃣ 𝗘𝗺𝗯𝗲𝗱𝗱𝗲𝗱 𝗰𝗼𝗻𝗱𝘂𝗰𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗻𝗮𝗻𝗼𝗳𝗶𝗯𝗲𝗿𝘀 – act as high-speed highways for Li-ion diffusion, enabling faster charge/discharge and higher utilization of active material.
These are just a couple of the strategies we use to enhance our LMFP conductivity. In our next post, we’ll share more insights into additional innovations that further improve conductivity.
📌 Stay tuned for more!
#LMFP #BatteryMaterials #EnergyStorage #EVBatteries #BatteryInnovation #CathodeMaterials #LithiumIonBatteries #ElectricVehicles #EnergyTech #BatteryResearch